Automotive CAN Bus Protocol Specification
Automotive CAN Bus Protocol Specification
In the automotive electronics industry, CAN is used to connect engine control units, sensors, square brake systems, etc., with transmission speeds up to 1 Mbit/s. At the same time, CAN can be installed in automotive-themed electronic control systems, such as vehicle lights, Electrical windows, etc., are used instead of wiring wiring devices. CAN is a serial communication protocol, which can effectively support real-time control of segments with high security levels.
The purpose of the technical specifications is to establish compatibility between any two CAN instruments. We do some analysis from the data link layer and the physical layer:
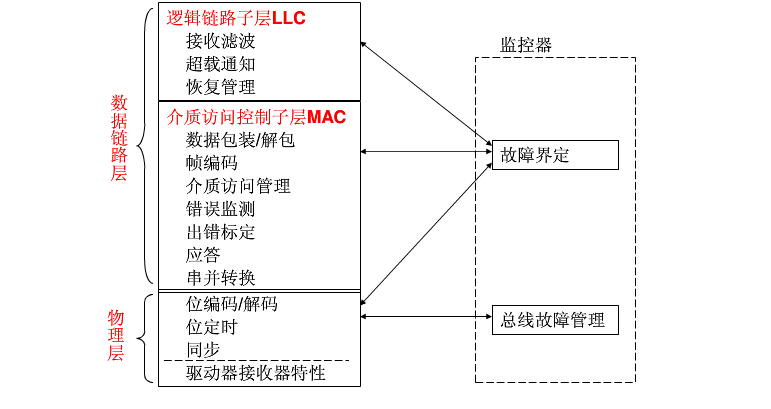
In the previous CAN protocol specification, the services and functions of the LLC sublayer and the MAC sublayer of the data link layer are interpreted as "object layer" and "transport layer", respectively.
The scope of the logical link control sublayer LLC is as follows:
1. Serving remote data requests and data transmission;
2. Determine which message is actually received by the LLC sublayer;
3. Provide means for reply management and overload notification.
The role of the MAC sublayer is mainly to convey rules, that is, control frame structure, execution arbitration, error detection, error calibration, and fault definition. Some common functions of bit timing can also be seen as part of the MAC sublayer, which acts to actually transfer bits between different nodes based on all electrical properties.
Has the following properties:
- the priority of the message
- Guaranteed delay time
- Flexible setting
- Multi-point acceptance of time synchronization
- Coherence of data within the system
-Multi-host
- Error detection and error calibration
- Automatically retransmitted corrupted messages as soon as the bus is idle
- Distinguish between temporary and permanent errors of the node, and can automatically close the wrong node of the layered CAN structure by the OSI reference model.
he layer structure according to the IOS/OSI reference model has the following functions:
- The physical layer defines how the signal is actually transmitted, thus involving interpretation of bit time, bit coding, synchronization. The technical specifications do not define the driver/receiver characteristics of the physical layer to allow for optimization of the transmit media and signal levels based on their application.
The -MAC sublayer is the core of the CAN protocol. He provides the received message to the LLC sublayer and receives the message from the LLC sublayer. The MAC sublayer is responsible for message framing, arbitration, response, error monitoring, and calibration. The MAC sublayer is also referred to as a fault-defined management entity. Therefore, the fault is defined as a self-built mechanism, which distinguishes between permanent faults and short-term disturbances.
- LLC sub-layer design message filtering, overload notification, and recovery management.
